The procurement function is vital to business success, but is highly susceptible to external influences.
The procurement function is vital to business success, but is highly susceptible to external influences. These can disrupt supply chains, increase costs, and introduce procurement risk factors. Political shifts, economic fluctuations, and technological advancements frequently impact internal and external factors affecting procurement strategies.
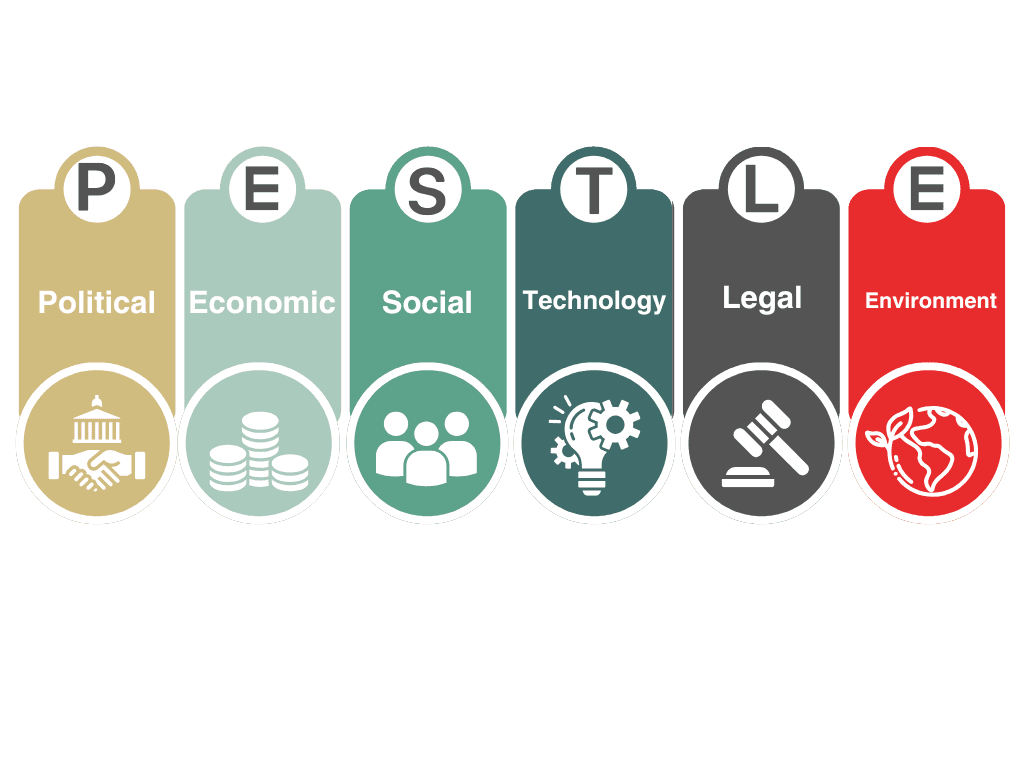
Using a PESTLE framework examines Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental dimensions. Using this framework organizations can better understand these factors and develop strategies to mitigate risks.
This article explores how external factors impact the procurement function. It offers practical solutions to strengthen resilience and address procurement risk factors.
Political and Legal Factors Affecting Procurement
Political and legal changes can create significant challenges for procurement teams. This influences supplier relationships, compliance requirements, and overall strategies. Staying informed about shifting regulations and geopolitical dynamics is essential for mitigating procurement risk factors.
Domestic Political and Legal Changes
In the UK, political decisions and legal reforms directly shape procurement practices.
- The Public Services (Social Value) Act 2012 ensures that public sector contracts evaluate social and environmental benefits. This drives procurement teams to adopt more sustainable strategies.
- The Modern Slavery Act 2015 requires businesses to ensure ethical sourcing and publish statements on how they address modern slavery risks within their supply chains.
Moreover, regulatory reforms often affect compliance costs. A 2023 report by the CIPS (Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply) highlighted that 68% of UK procurement professionals found it increasingly challenging to stay compliant with evolving domestic policies.
Global Political and Legal Dynamics
On a global scale, political instability and evolving trade agreements often disrupt supply chains.
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict has significantly impacted energy and commodity markets, driving up procurement costs for critical resources like natural gas.
- The US-China trade war imposed tariffs on $550 billion worth of goods, forcing companies to re-evaluate supplier relationships and sourcing strategies.
- The European Green Deal sets stringent sustainability goals, requiring procurement teams to work with environmentally compliant suppliers.
Case in Point: Brexit’s Continuing Impact
Brexit has fundamentally altered trade dynamics for UK businesses. According to a 2023 British Chambers of Commerce survey, 77% of firms reported ongoing difficulties complying with post-Brexit regulations. For procurement teams, this has meant longer lead times and higher administrative costs. Additionally, the UK’s new trade agreements with countries like Australia and New Zealand provide opportunities but require thorough analysis to leverage cost advantages.
Economic Factors Affecting Procurement
Economic conditions significantly influence the procurement function by impacting costs, supplier relationships, and operational strategies.
Inflation and Rising Costs
In 2023, UK inflation rates remained high at 8.7%. This was reflected by rising raw material costs across industries like construction and manufacturing. Procurement teams had to renegotiate supplier contracts and explore alternative sourcing to control costs.
Currency Volatility
Changing exchange rates can increase risks for businesses. For example, the pound dropped 15% against the dollar in 2022. This situation is particularly challenging for companies that rely on international suppliers. Currency hedging strategies have become essential to mitigate financial exposure.
Energy Costs and Supply Chain Disruptions
Soaring energy prices continue to affect industries like utilities and retail. Procurement teams are prioritizing long-term contracts and domestic suppliers to manage risks.
Social Factors Affecting Procurement
Shifting societal expectations and consumer behaviors are external factors that increasingly shape procurement strategies.
Demand for Sustainability
Sustainability is no longer optional. According to a 2023 Deloitte survey, 55% of consumers prefer brands with sustainable supply chains. This prompts procurement teams to prioritize eco-friendly suppliers and ethically sourced materials.
Emphasis on Diversity
Procurement strategies now include commitments to supplier diversity. Many organizations aim to work with small businesses or minority-owned enterprises to reflect social responsibility and meet evolving customer expectations.
Cultural Sensitivities in Global Supply Chains
In international procurement, understanding cultural nuances can enhance supplier relationships and negotiation outcomes. For instance, respecting regional practices can improve trust and lead to stronger partnerships.
Strategies to Align with Social Trends
- Partner with suppliers certified in sustainable or diverse sourcing.
- Use tools like sustainability scores to evaluate supplier practices.
Technological Factors Affecting Procurement
Advancements in technology are reshaping the procurement function, influencing supplier management, cost control, and operational efficiency.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation tools streamline repetitive tasks like invoice processing, while AI enhances decision-making through predictive analytics. According to a Gartner survey conducted in 2024, 72% of procurement leaders are prioritizing the integration of GenAI into their strategies
Supply Chain Management Platforms
Cloud-based systems such MyAchilles simplify processes, improve transparency, and support compliance.
Strategies to Leverage Technology
- Implement AI-driven tools to enhance forecasting and supplier performance analysis.
- Adopt e-procurement systems to streamline workflows and reduce manual errors.
Environmental Factors Affecting Procurement
Environmental considerations have become a critical component of procurement strategies as climate change, resource scarcity, and natural disasters disrupt supply chains.
Climate Change and Resource Scarcity
Extreme weather events and resource shortages pose significant challenges. For example, the 2022 European drought disrupted agricultural supply chains, reducing crop yields and driving up food prices. Procurement teams must account for such risks by sourcing from diverse regions and prioritizing sustainable practices.
Sustainability Regulations
Governments are implementing stricter sustainability requirements, such as the European Union’s Green Deal. This deal aims to make Europe carbon-neutral by 2050. Procurement teams are increasingly expected to evaluate suppliers’ environmental impact and choose those with strong sustainability credentials.
Natural Disasters and Supply Chain Resilience
Natural disasters, such as the 2023 Turkey-Syria earthquakes, highlight the need for resilient supply chains. Procurement professionals are now focusing on spreading supplier risk geographically to minimize disruptions.
Strategies for Environmental Risks
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Evaluate suppliers’ environmental practices and vulnerability to climate risks.
- Diversify Suppliers: Reduce dependency on high-risk regions to build supply chain resilience.
- Adopt Green Procurement Policies: Prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices and certifications.
Building Resilience in Procurement
External challenges play a key role in shaping the procurement function. By leveraging tools like the PESTLE framework, organizations can systematically analyze these challenges and develop strategies to mitigate procurement risk factors effectively.
Procurement teams that proactively address external factors affecting procurement are better positioned to build resilient, future-ready supply chains.
To navigate an ever-changing landscape, businesses must stay informed, embrace innovation, and prioritize sustainability in their procurement strategies.
Contact us today for support in improving your supply chain transparency and mitigating risk.